UT1750AR12WCC Ver la hoja de datos (PDF) - Aeroflex UTMC
Número de pieza
componentes Descripción
Fabricante
UT1750AR12WCC Datasheet PDF : 56 Pages
| |||
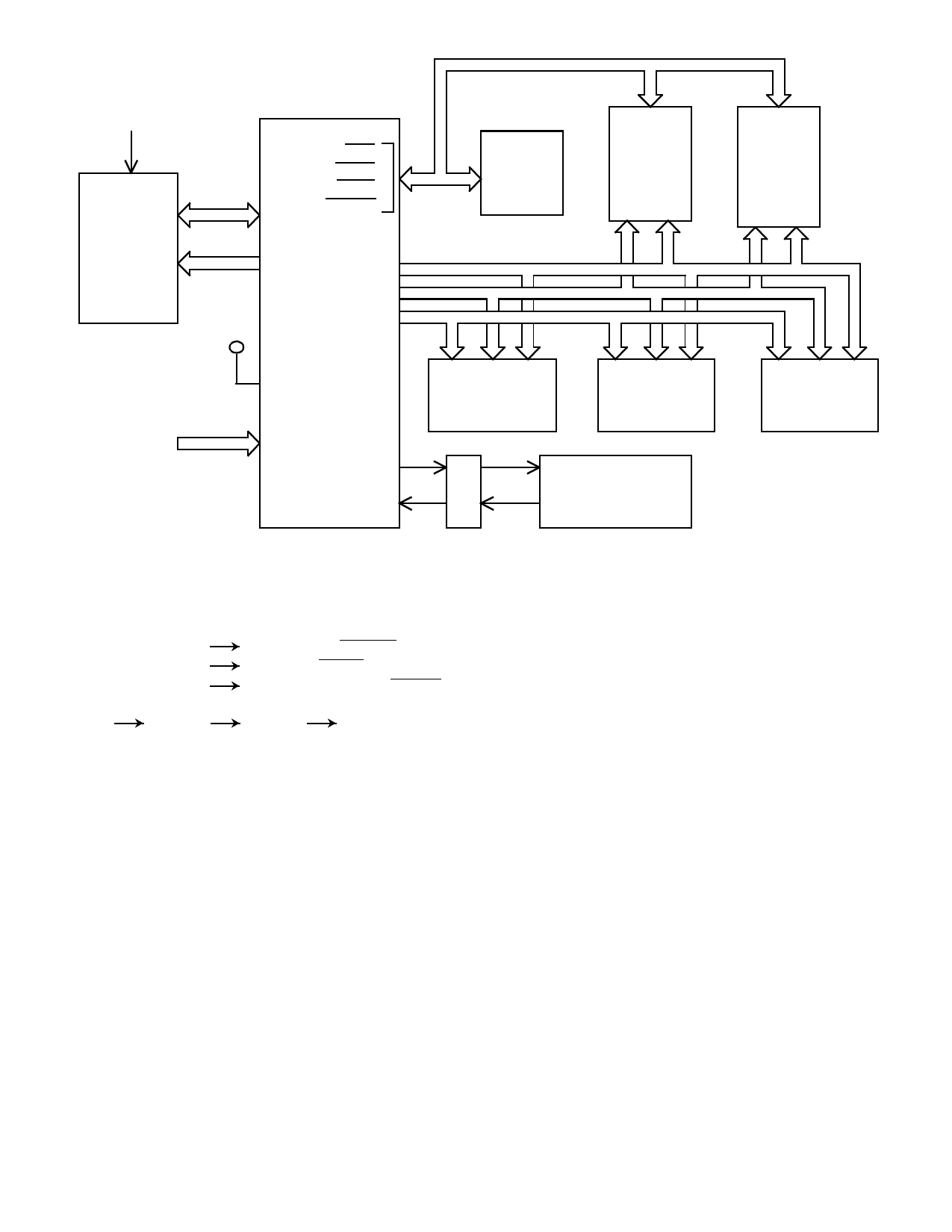
CONTAINS RISC MACROS TO
EMULATE THE MIL-STD-1750A
ISA
1750
EMULATION
ROM
(8K X 16)
BRQ
BGNT
BUSY
16
RISC BGACK
DATA
16
+5V
RISC
ADD OP ADD
OP DATA
CONTROL
4
BUS
ARBITER
DMA
DEVICE
#1
1553
I/F
16
16
6
USER-
DEFINED
8
SYSTEM
INTERRUPTS
M1750
UT1750AR
1750
PROGRAM/DATA
MEMORY
I/O
DEVICE #1
UART
X
I/F
C
V
R
MIL-STD-1750
PROGRAMMER’S
CONSOLE
Figure 5. The UT1750AR in the MIL-STD-1750 Mode of Operation
DMA
DEVICE
#2
I/O
DEVICE #2
The next three RISC address bits (RA16-RA18) are user-
definable discrete outputs. These outputs are defined as:
RA16/OD3
DMA enable (DMAEN)
RA17/OD2
power-up (GOOD)
RA18/OD1
start-up ROM enable (SUREN)
After reset these signals will be in the following states:
RA16
1, RA17
0, RA18
0.
When the UT1750AR operates in the MIL-STD-1750 mode, it
generates an address on the Operand address bus for the next
1750 instruction. If the UT1750AR has just been initialized or
has just been reset, the first memory location placed on the
Operand Address Bus is 0000H; this instruction is the first one
fetched from the 1750 memory. After this instruction is fetched
and entered into the UT1750AR, the UT1750AR uses the
opcode to “map” or point to a specific address in the RISC
memory. Since the RISC PROM programming provides 1750
emulation capability, this address in RISC memory contains a
specific RISC-coded macro allowing the UT1750AR to perform
the requisite 1750 function.
When the UT1750AR begins executing this RISC macro for
1750 emulation, the UT1750AR begins to operate as if it were
in the RISC mode (see the previous section on RISC mode of
operation). The processor cycles of all the RISC instructions
that make up the particular macro are executed as if the
UT1750AR were operating purely as a RISC.
During RISC macro execution for the MIL-STD-1750
instruction, the internal registers of the UT1750AR hold the
intermediate results from the execution of the RISC instructions.
When the macro is complete, the UT1750AR’s registers contain
the data the MIL-STD-1750A instruction requires.
If the UT1750AR receives an interrupt during RISC macro
execution, the RISC macro completes execution before the
UT1750AR recognizes the interrupt. This is similar to
completing a single 1750 instruction rather than allowing its
interruption. The only exception is with the multiple-word
MOV 1750 instruction. For this instruction, the UT1750AR
interrupts macro execution after transferring the current word.
After the RISC macro is complete, all the UT1750AR’s internal
registers, including the status registers and/or memory locations,
contain the results of the MIL-STD-1750A instruction that has
just completed execution. The UT1750AR now fetches the next
1750 instruction from Operand memory and the process repeats.
13