T5760 Ver la hoja de datos (PDF) - Atmel Corporation
Número de pieza
componentes Descripción
Fabricante
T5760 Datasheet PDF : 32 Pages
| |||
T5760 / T5761
Bit-Check Mode
In bit-check mode the incoming data stream is examined
to distinguish between a valid signal from a correspond-
ing transmitter and signals due to noise. This is done by
subsequent time frame checks where the distances be-
tween 2 signal edges are continuously compared to a
programmable time window. The maximum count of this
edge-to-edge tests before the receiver switches to receiv-
ing mode is also programmable.
Configuring the Bit Check
Assuming a modulation scheme that contains 2 edges per
bit, two time frame checks are verifying one bit. This is
valid for Manchester, Bi-phase and most other modula-
tion schemes. The maximum count of bits to be checked
can be set to 0, 3, 6 or 9 bits via the variable NBit-check in
the OPMODE register. This implies 0, 6, 12 and 18 edge
to edge checks respectively. If NBit-check is set to a higher
value, the receiver is less likely to switch to receiving
mode due to noise. In the presence of a valid transmitter
signal, the bit check takes less time if NBit-check is set to
a lower value. In polling mode, the bit-check time is not
dependent on NBit-check. Figure 12 shows an example
where 3 bits are tested successfully and the data signal is
transferred to Pin DATA.
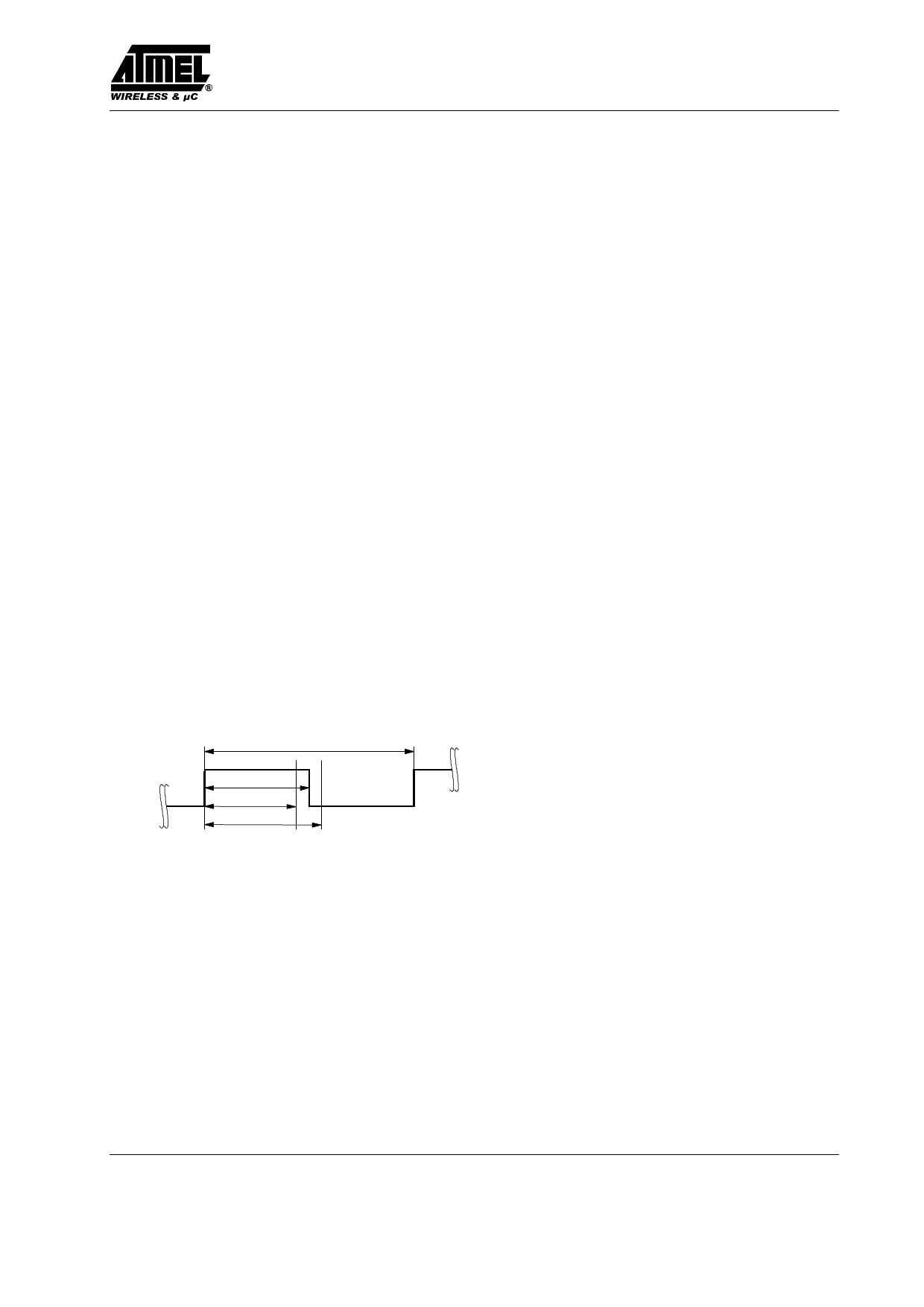
According to figure 13, the time window for the bit check
is defined by two separate time limits. If the edge-to-edge
time tee is in between the lower bit-check limit TLim_min
and the upper bit-check limit TLim_max, the check will be
continued. If tee is smaller than TLim_min or tee exceeds
TLim_max, the bit check will be terminated and the re-
ceiver switches to sleep mode.
1/fSig
Dem_out
tee
TLim_min
TLim_max
Figure 10. Valid time window for bit check
For best noise immunity it is recommended to use a low
span between TLim_min and TLim_max. This is achieved us-
ing a fixed frequency at a 50% duty cycle for the
transmitter preburst. A ‘11111...’ or a ‘10101...’ sequence
in Manchester or Bi-phase is a good choice concerning
that advice. A good compromise between receiver sensi-
tivity and susceptibility to noise is a time window of
± 25% regarding the expected edge-to-edge time tee. Us-
ing pre-burst patterns that contain various edge-to-edge
time periods, the bit-check limits must be programmed
according to the required span.
The bit-check limits are determined by means of the for-
mula below.
TLim_min = Lim_min × TXClk
TLim_max = (Lim_max –1) × TXClk
Lim_min and Lim_max are defined by a 5-bit word each
within the LIMIT register.
Using above formulas, Lim_min and Lim_max can be de-
termined according to the required TLim_min, TLim_max
and TXClk. The time resolution defining TLim_min and
TLim_max is TXClk. The minimum edge-to-edge time tee
(tDATA_L_min, tDATA_H_min) is defined according to the
chapter ‘Receiving Mode’. The lower limit should be set
to Lim_min ≥ 10. The maximum value of the upper limit
is Lim_max = 63.
If the calculated value for Lim_min is < 19, it is recom-
mended to check 6 or 9 bits (NBit-check) to prevent
switching to receiving mode due to noise.
Figures 14, 15 and 16 illustrate the bit check for the bit-
check limits Lim_min = 14 and Lim_max = 24. When
the IC is enabled, the signal processing circuits are en-
abled during TStartup. The output of the ASK/ FSK
demodulator (Dem_out) is undefined during that period.
When the bit check becomes active, the bit-check counter
is clocked with the cycle TXClk.
Figure 14 shows how the bit check proceeds if the bit-
check counter value CV_Lim is within the limits defined
by Lim_min and Lim_max at the occurrence of a signal
edge. In figure 15 the bit check fails as the value CV_lim
is lower than the limit Lim_min. The bit check also fails
if CV_Lim reaches Lim_max. This is illustrated in
figure 16.
Rev. A2, 19-Oct-00
9 (32)
Preliminary Information