21555 Ver la hoja de datos (PDF) - Intel
Número de pieza
componentes Descripción
Fabricante
21555 Datasheet PDF : 60 Pages
| |||
Non-Transparent PPB
It was a primary goal of the PCI-to-PCI bridge architecture that a PPB be transparent to devices
and device drivers. For example, no changes are needed to a device driver when a PCI peripheral is
located behind a PPB. Once configured during system initialization, a PPB operates without the aid
of a device driver. A PPB does not require a device driver of its own since it does not have any
resources that must be managed by software during run-time. This requirement for transparency
forced the usage of a flat addressing model across PCI-to-PCI bridges. This means that a given
physical address exists at only one location in the PCI bus hierarchy and that this location may be
accessed by any device attached at any point in the PCI bus hierarchy. As a consequence, it is not
possible for a PPB to isolate devices or address ranges from access by devices on the opposite
interface of a PPB. The PPB architecture assumes that the resources of any device in a PCI system
are configured and managed by the host processor.
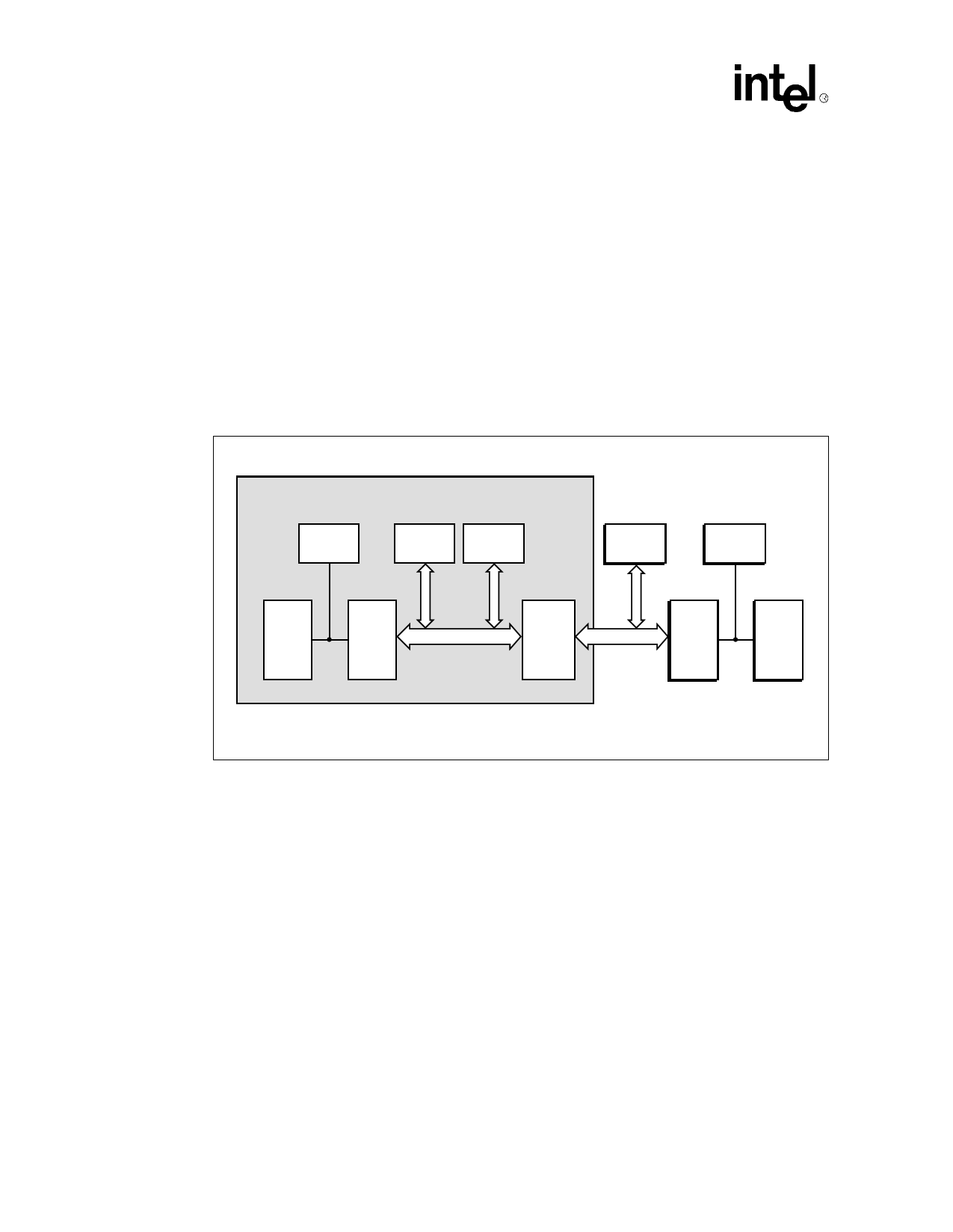
However, there are applications where the transparency of a PCI-to-PCI bridge is not desired. For
example, Figure 1 shows a hypothetical PCI add-in card used for an intelligent subsystem
application.
Figure 1. 21555 Intelligent Controller Application
Intelligent Subsystem
DRAM/
ROM
PCI
Device
PCI
Device
PCI
Device
Memory
Local
CPU
CPU-
PCI
Bridge
PCI Bus
Intel®
21555
Device
PCI Bus
Host
Core
Logic
Host
CPU
A8826-01
Assume that the local processor on the add-in card is used to manage the resources of the devices
attached to the add-in card’s local PCI bus. Assume also that it is desirable to restrict access to
these same resources from other PCI bus masters in the system and from the host processor. In
addition, there is a need to resolve address conflicts that may exist between the host system and the
local processor. The non transparency of the 21555 is perfectly suited to this kind of configuration,
where a transparent PCI-to-PCI bridge is problematic.
Because the 21555 is not transparent, the device driver for the add-in card must be aware of the
presence of the 21555 and manage its resources appropriately. The 21555 allows the entire
subsystem to appear as a single virtual device to the host. This enables configuration software to
identify the appropriate driver for the subsystem.
With a transparent PCI-to-PCI bridge, a driver does not need to know about the presence of the
bridge and manage its resources. The subsystem appears to the host system as individual PCI
devices on a secondary PCI bus, not as a single virtual device.
Table 1 shows a comparison between a 21555 and a standard transparent PCI-to-PCI bridge.
6
Datasheet