MAX1661 Ver la hoja de datos (PDF) - Maxim Integrated
Número de pieza
componentes Descripción
Fabricante
MAX1661 Datasheet PDF : 16 Pages
| |||
Serial-to-Parallel/Parallel-to-Serial Converters and
Load-Switch Controllers with SMBus Interface
START
SMBCLK
SMBDATA
tLOW:SS
tBUF
ALERT
START-STOP INTERRUPT
ALERT RESPONSE ADDRESS
(0001100)
SLAVE
ACKNOWLEDGE
(ACK)
STOP
DATA LINE HELD
LOW BY SLAVE
ACTUAL SLAVE ADDRESS
(0100000 IN THIS EXAMPLE)
DUMMY BIT (1)
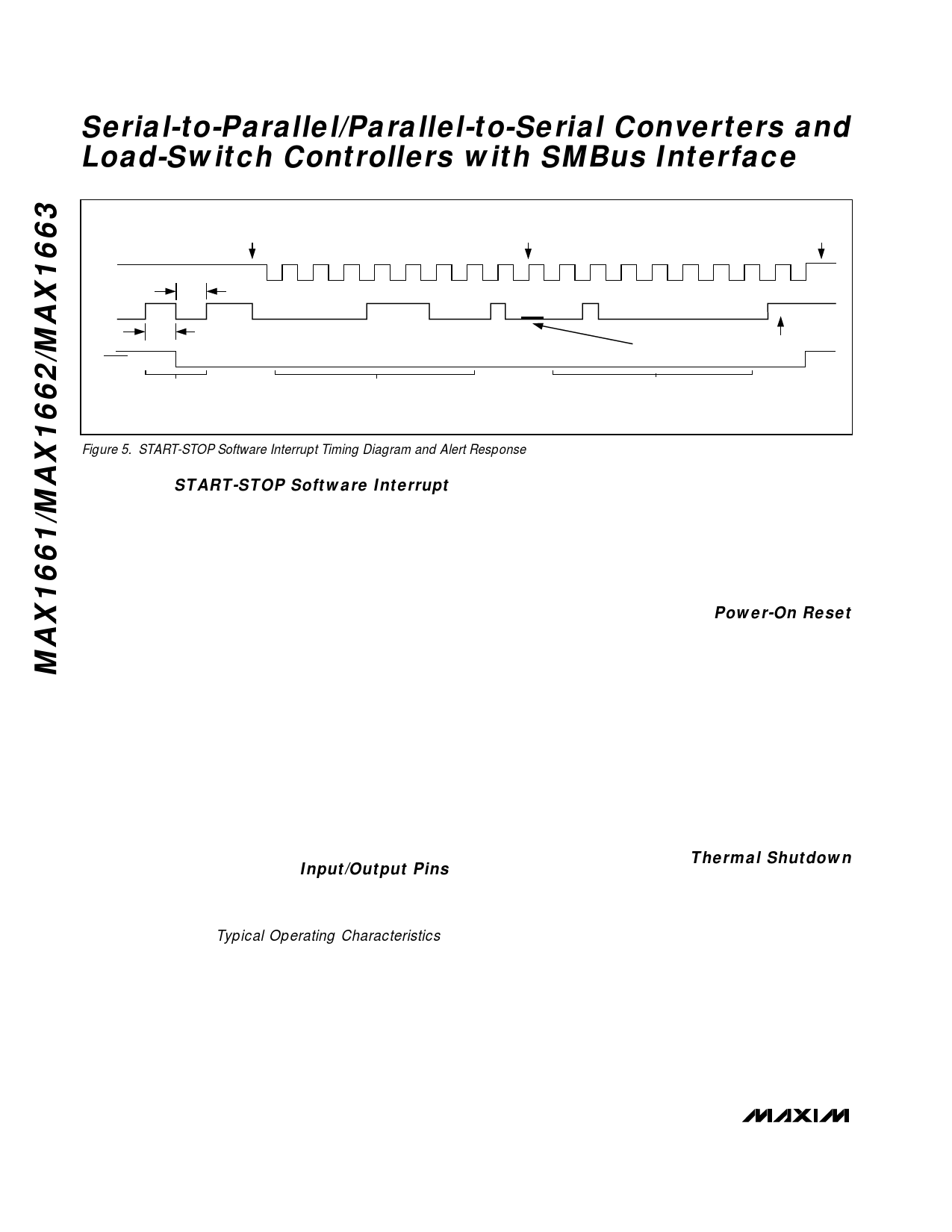
Figure 5. START-STOP Software Interrupt Timing Diagram and Alert Response
START-STOP Software Interrupt
The START-STOP interrupt is a method for the slave
device to initiate a signal over the 2-wire interface with-
out the need for a third (interrupt) wire. A START-STOP
interrupt is a start condition followed by a stop condi-
tion; in other words, SMBDATA goes low and then high
with SMBCLK high (Figure 5 shows the START-STOP
interrupt and a subsequent Alert Response transmis-
sion used to clear the interrupt). The START-STOP
function can be disabled (masked) by setting the data
register mask SS (bit 6) high.
In order to avoid bus collisions, the START-STOP inter-
rupt will not occur when the bus is busy. If the device
begins a start condition simultaneously with another
transmitter on the bus, it recognizes the falling SMB-
CLK as a collision and re-transmits the interrupt when
the bus becomes available. Upon thermal shutdown or
a transition on an I/O line, the device issues only one
START-STOP interrupt, and won’t repeat it unless there
has been a collision. However, thermal-shutdown faults,
not being edge triggered, may result in a continuous
stream of START-STOP bits.
Input/Output Pins
Each input/output (I/O) is protected by an internal
20mA (typical) current-limit circuit. The I/O current limit
depends on the supply voltage and the voltage applied
to the I/O pins (see Typical Operating Characteristics).
The typical I/O bias current is 0.5µA to VI/O_ = 28V.
The ability of the I/Os to sink current depends on VCC
as well as the voltage on the I/O. Typical pull-down on-
resistance at VCC = 2.7V and 5.5V is 106Ω and 66Ω,
respectively. I/O source and sink capability can affect
the rise and fall times of external power MOSFETs com-
monly used in power-switching applications. Other fac-
tors include the VGS, the input capacitance of the MOS-
FET, and the pull-up resistor value used in the circuit.
Typical MOSFET gate capacitance ranges from 150pF
to 2000pF. Increasing the RC time constant slows down
the MOSFET’s response, but provides for a smoother
transition.
Power-On Reset
The power-on reset circuit keeps the external MOSFETs
off during a power-up sequence. When the supply volt-
age falls below the power-on reset threshold voltage,
the MAX1662/MAX1663’s outputs reset to a high-
impedance state, and the MAX1661’s outputs reset to a
low state. During the initial power-up sequence, as VCC
increases, the ALERT pin goes low and then high,
which indicates the device is powered on. The time
between the low and high state on ALERT is the power-
on delay time. Below VCC = 0.8V (typical) the POR
states can’t be enforced, and the I/O pins of all ver-
sions exhibit increasingly weak pull-down current capa-
bility, eventually becoming high impedance.
Thermal Shutdown
These devices have internal thermal-shutdown circuitry
that turns off all output stages (I/O pins) when the junc-
tion temperature exceeds +140°C typical. Thermal
shutdown only occurs during an overload condition on
the I/O pins. The device cycles between thermal shut-
down and the overcurrent condition until the overload
condition is removed. This could cause a sustained
START-STOP interrupt and, in the extreme case, tie up
the master controller. However, the device asserts
ALERT low, indicating this fault status.
10 ______________________________________________________________________________________