LT8580 Ver la hoja de datos (PDF) - Linear Technology
Número de pieza
componentes Descripción
Fabricante
LT8580
LT8580 Datasheet PDF : 32 Pages
| |||
LT8580
Applications Information
SEPIC Converter Component Selection
(Coupled or UnCoupled Inductors)
VIN
L1
• 22µH
C1
1µF
D1
9V TO 16V
487k
L2
22µH
VOUT
12V
240mA
CIN
4.7µF
VIN
SW
SHDN
FBX
LT8580
• RFBX
130k
SYNC
VC
RT GND SS
RC
16.2k
RT
84.5k
CSS
CC
0.22µF
1nF
COUT
4.7µF
CF
22pF
8580 F16
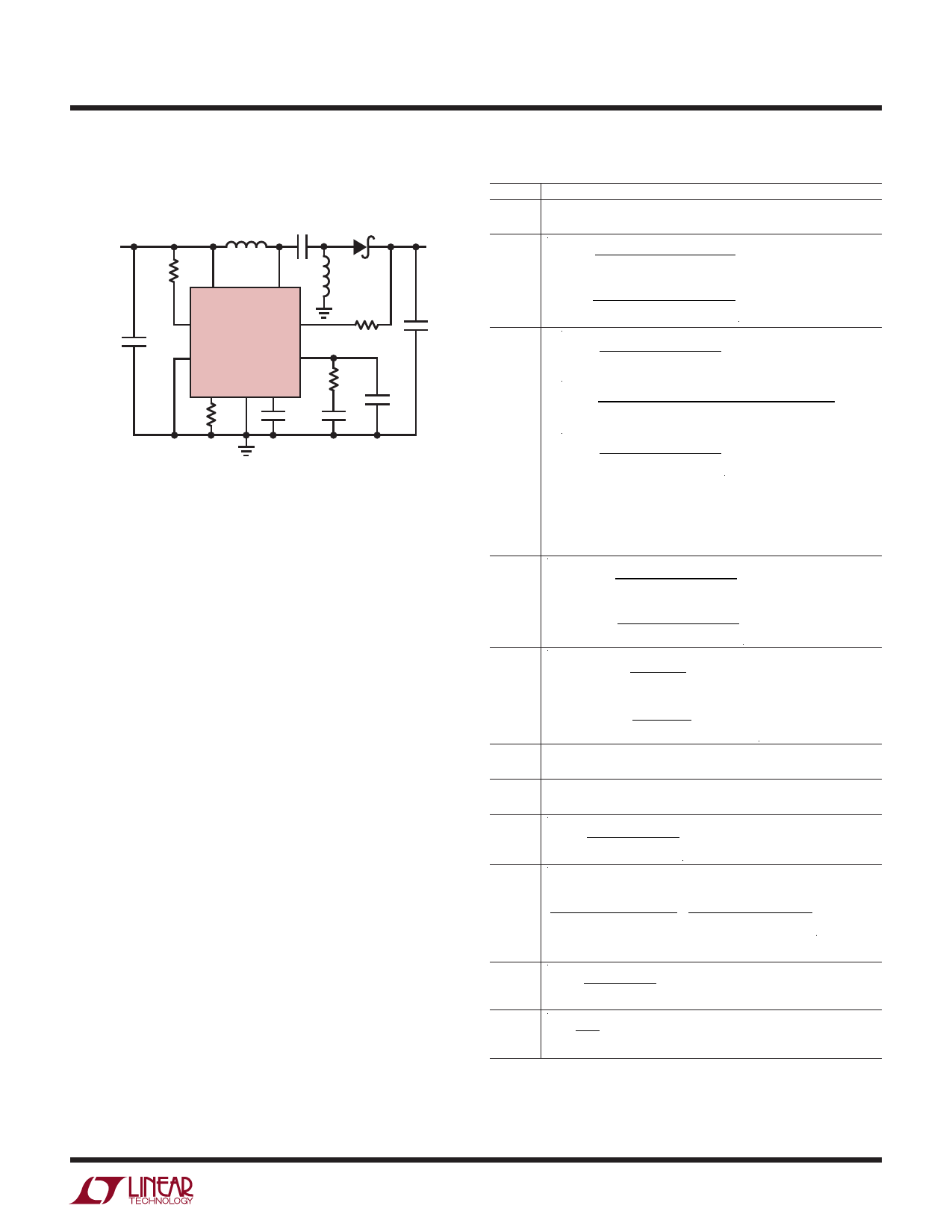
Figure 16. SEPIC Converter: The Component Values and Voltages
Given Are Typical Values for a 1MHz, 9V to 16V Input to 12V
Output SEPIC Converter
The LT8580 can also be configured as a SEPIC, as shown
in Figure 16. This topology allows for positive output volt-
ages that are lower, equal or higher than the input volt-
age. Output disconnect is inherently built into the SEPIC
topology, meaning no DC path exists between the input
and output due to capacitor C1.
Table 5. SEPIC Design Equations
PARAMETERS/EQUATIONS
Step 1: Pick VIN, VOUT and fOSC to calculate equations below
Inputs
Step 2:
DC
DCMAX
=
VIN(MIN)
VOUT + 0.5 V
+ VOUT + 0.5 V– 0.4V
DCMIN
=
VIN(M AX )
VOUT + 0.5 V
+ VOUT + 0.5 V– 0.4V
Step 3:
L
LTYP
=
(VIN(MIN) – 0.4V) • DCMAX
fOSC • 0.3A
(1)
LMIN
=
1.25
•
(VIN(MIN) – 0.4V) • (2 • DCMAX
(DCMAX − 300nS • fOSC ) • fOSC •
– 1)
(1–
DCMAX
)
(2)
Step 4:
IRIPPLE
Step 5:
IOUT
LMAX
=
(VIN(MIN) – 0.4V) • DCMAX
fOSC • 0.08 A
(3)
• Solve equations 1, 2 and 3 for a range of L values
• The minimum of the L value range is the higher of LTYP and LMIN
• The maximum of the L value range is LMAX
• L = L1 = L2 for coupled inductors
• L = L1|| L2 for uncoupled inductors
IRIPPLE(MIN)
=
(VIN(MIN)
– 0.4V)
fOSC • L
•
DCMAX
IRIPPLE(M AX )
=
(VIN(MAX) – 0.4V)
fOSC • L
• DCMIN
( ) IOUT(MIN)
=
⎛
⎜1A
−
IRIPPLE(MIN)
⎞
⎟
•
⎝
2⎠
1− DCMAX
Table 5 is a step-by-step set of equations to calculate com-
ponent values for the LT8580 when operating as a SEPIC
converter. Input parameters are input and output voltage,
and switching frequency (VIN, VOUT and fOSC, respectively).
Refer to the Applications Information section for further
information on the design equations presented in Table 5.
Variable Definitions:
VIN = Input Voltage
VOUT = Output Voltage
Step 6:
D1
Step 7:
C1
Step 8:
COUT
Step 9:
CIN
( ) IOUT(MAX)
=
⎛
⎜1A
−
IRIPPLE(MAX
)
⎞
⎟
•
⎝
2⎠
1− DCMIN
VR > VIN + VOUT; IAVG > IOUT
C1 ≥ 1µF; VRATING ≥ VIN
COUT
≥
IOUT(MIN) • DCMAX
fOSC • 0.005 • VOUT
CIN ≥ CVIN + CPWR ≥
1A • DCMAX
+
IRIPPLE(M AX )
40 • fOSC • 0.005 • VIN(MIN) 8 • fOSC • 0.005 • VIN(MAX)
DC = Power Switch Duty Cycle
fOSC = Switching Frequency
IOUT = Maximum Average Output Current
IRIPPLE = Inductor Ripple Current
Step 10:
RFBX
• Refer to the Capacitor Selection Section for definition of CVIN and CPWR
RFBX
=
VOUT − 1.204V
83.3µA
Step 11:
RT
RT
= 85.5
fOSC
–1 ;
fOSC
in MHz and RT
in kΩ
Note 1: This table uses 1A for the peak switch current. Refer to the
Electrical Characteristics Table and Typical Performance Characteristics
plots for the peak switch current at an operating duty cycle.
Note 2: The final values for COUT, CIN and C1 may deviate from the
previous equations in order to obtain desired load transient performance.
8580f
For more information www.linear.com/LT8580
23